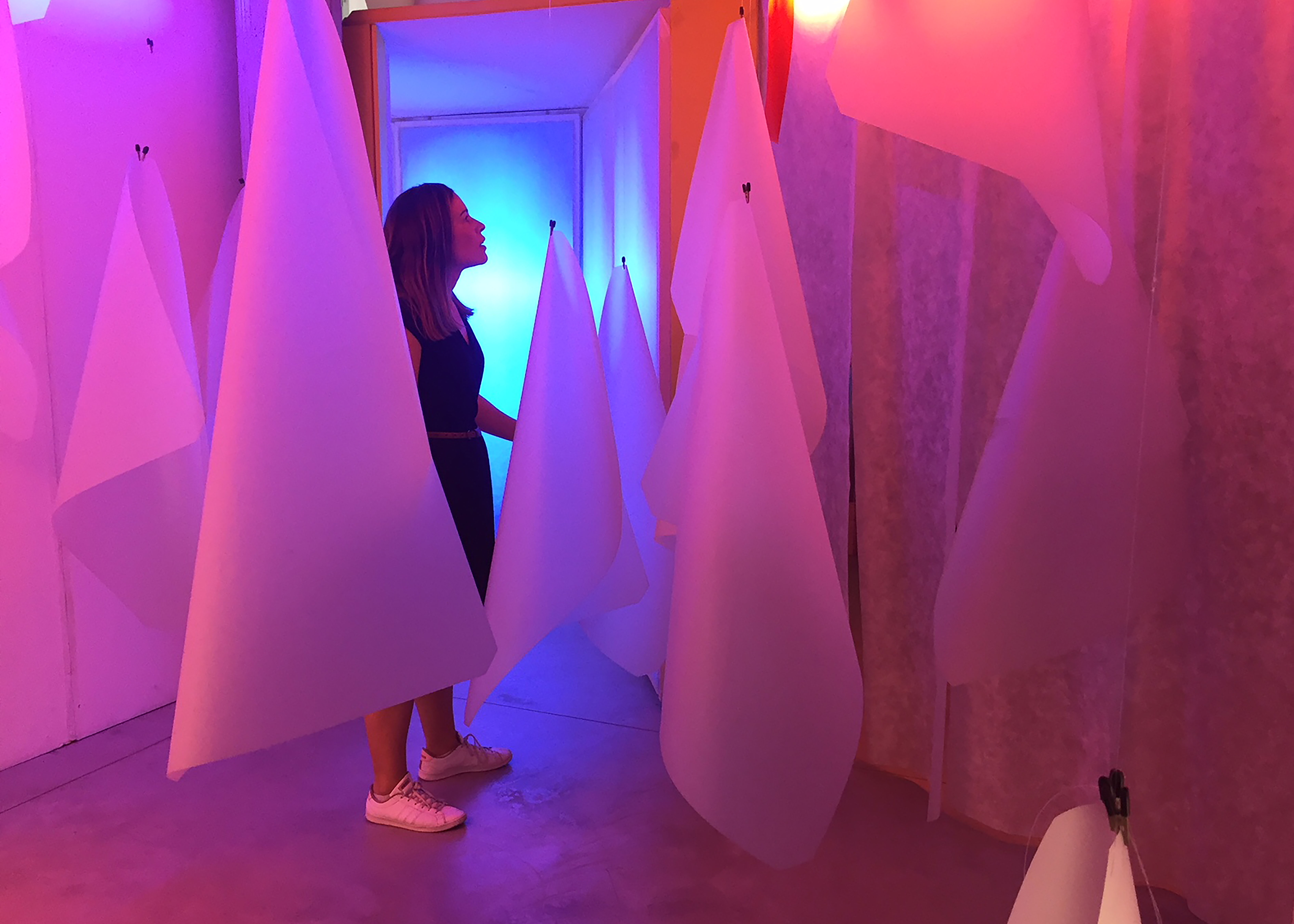
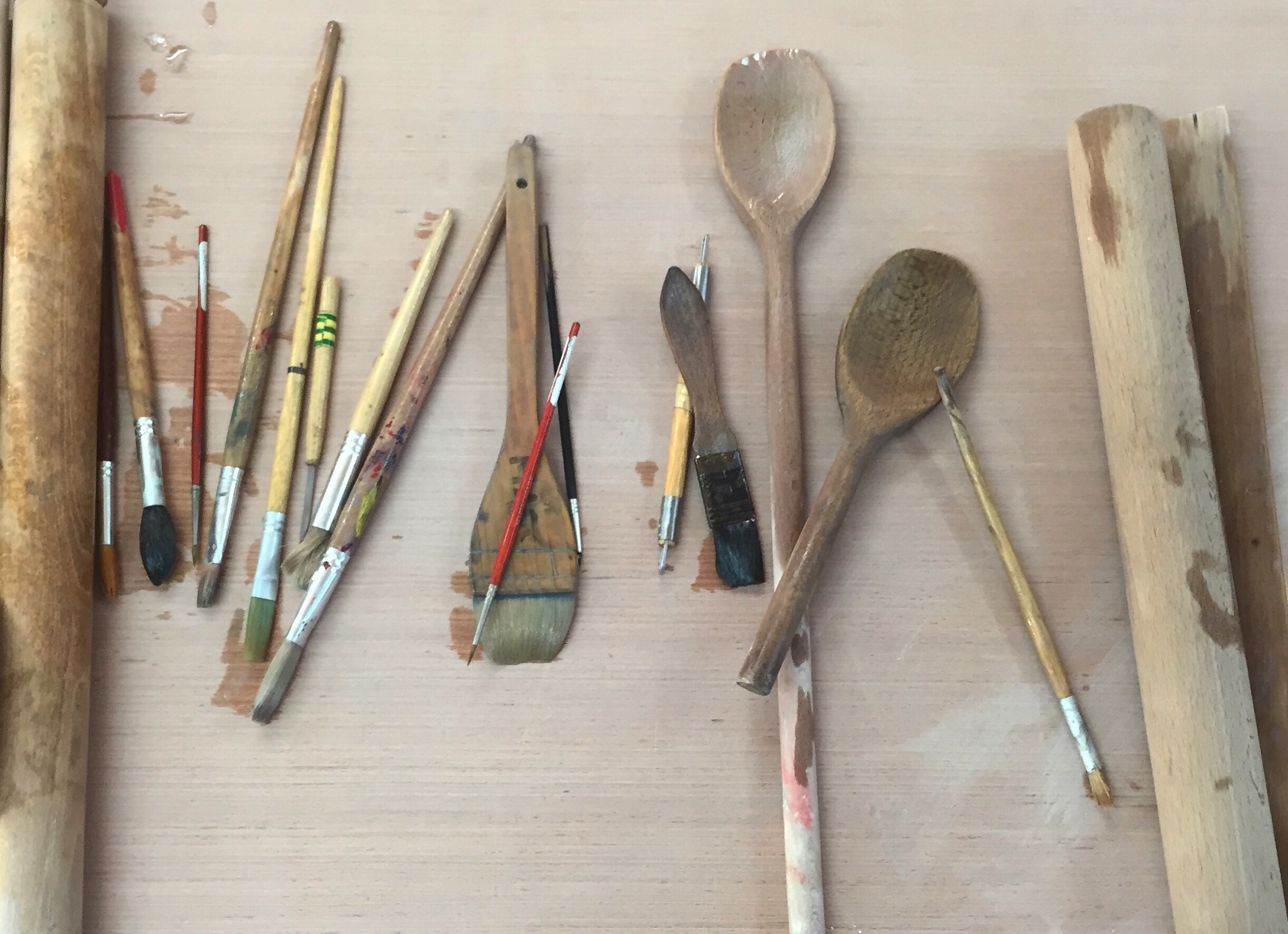
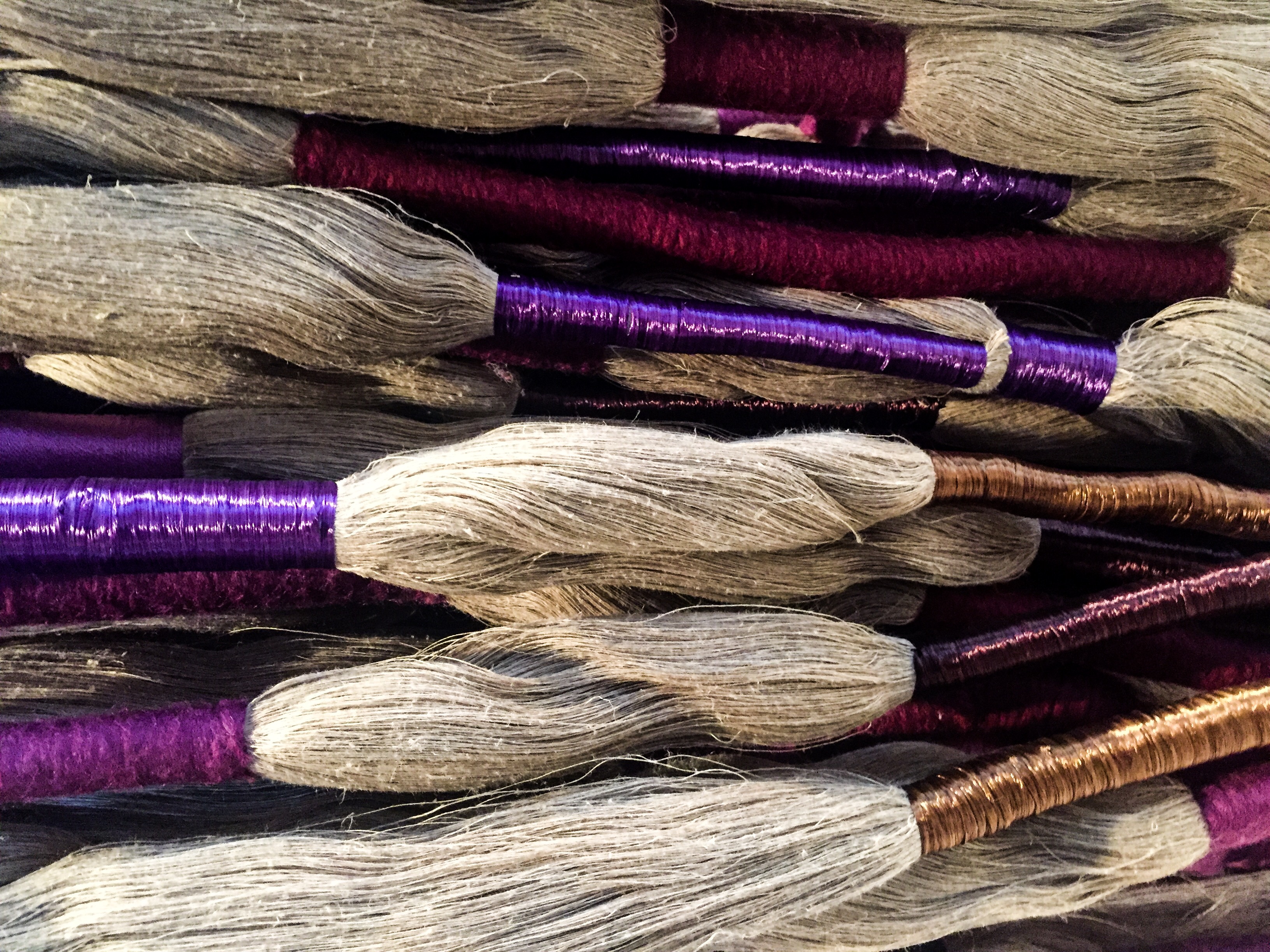
Earlier this month I was fortunate enough to visit the Loris Malaguzzi centre in Reggio Emilia. I was interested in learning more about the early childhood philosophy’s approach to children’s creativity, art and learning with materials. This post shares key ideas around the role of the ‘atelier’ in the Reggio Emilia approach. I also discuss my reflections on the Ray of Light atelier space at the centre. “Tools and materials make it possible for children to have experiences in which their thinking takes on different forms” (Dahlberg & Moss, 2010) The Atelier – a space for children’s creative experimentation Educators from Reggio Emilia often talk about the unpredictable nature of learning in which knowledge is formed through unexpected relationships and new connections. This understanding challenges the idea that education is a linear process of development. In Reggio Emilia preschools, the atelier is a creative studio for young children’s imagination, expression and experimentation that…
4 organisations exploring materials in innovative ways
This is a follow up to my recent post on the role of materials in children’s learning through art. If you have not read this already, I recommend checking it out before reading on. Here I present four different organisations – a university research centre, a design consultancy, a creative recycle centre and a children’s art studio – who are all exploring materiality in new and experimental ways. I selected these organisations as I am interested in thinking about how materials are being researched and considered in a collective way, among groups of people with diverse interests, skills and expertise. MIT Media Lab: Mediating Matter group (USA) I am a massive fan girl of the MIT Media Lab. For those of you who are not unfamiliar with this university research centre, it is an interdisciplinary lab ‘that encourages the unconventional mixing and matching of seemingly disparate research areas’ (MIT website, 2018).…
3 tips for scaffolding children’s play with materials
Children’s play with materials is important as it allows them to think and learn in different ways. As a child’s creativity is always limited by what they do and do not know, scaffolding can open up new opportunities for more complex learning over time. Scaffolding is a term that was first coined by Vygotsky (1978) who described the process as something that allows children to move their current level of understandings to a more advanced one. This process helps children to undertake activities that they usually would not be able to without the help of others. Teachers and parents often do a lot of scaffolding in children’s lives. They teach children how to brush their teeth, share with others and read. Children’s peers, technology and information resource like a YouTube video can also scaffold children’s learning in different ways. Scaffolding is important in children’s play with materials as it allows…
Ivan Illich on tools that support conviviality
In 1973 Ivan Illich, a Catholic priest and Professor at Penn State University, published his famous text, Tools for Conviviality. In the book, he argued for people’s need to take control of the tools and processes of production that shaped their lives. Illich believed that people’s ability to participate in these processes would allow them to live more meaningful lives. Read on to learn more about the key ideas explored in Tools for Conviviality. What did Illich see as society’s primary problem? Illich believed that the advancement in mechanical, mass and industrial production had removed a person’s free use of their natural abilities. This development had also come at the expense of an individual’s capacity to connect with themselves and others, leading to the deterioration of the fabric of community. Illich argued that people do not just need the ability to obtain things, they also need the ability to make the…
Simon Nicholson’s theory of loose parts
In 1972 Simon Nicholson, the son of artists Ben Nicholson and Barbara Hepworth, presented the idea that young children’s cultural participation comes from the presence of open-ended ‘loose part’ materials that can be transformed in different ways. This post explores the key principles of the theory, including key debates surrounding it. What is loose parts theory? The term ‘loose parts’ was coined by Simon Nicholson, an English architect and artist. The loose parts theory was first presented in Nicholson’s article ‘the theory of loose parts: An important principle for design methodology.’ This theory rejects the idea that creativity is a characteristic of a select few. Nicholson claimed that people have been misled to think that creating artworks and buildings is so difficult that only highly gifted people can do it. In opposition to this, Nicholson argues that all people, including young children, are capable of participating in the construction of culture. Loose parts…
Children’s creative learning through the art of Sheila Hicks
“It is so important to make every day. The discovery comes in the making.” Sheila Hicks Sheila Hicks is an American textile artist whose colourful, soft sculptures bring together material traditions from Western and non-Western cultures. I recently visited her exhibition ‘Lifelines,’ on display at the Centre Pompidou in Paris. I loved learning about her experimentation with colour and how this has been a constant creative force throughout her life-long textile practice. In this post, I draw on works from the exhibition to consider how these could be used as a starting point for children’s creative learning through play with materials. This post is part of a four-part series looking at how artist’s experimentation with materials can be used to support creative learning. If you have not already read the first explored the sculpture practice of César Baldaccini, check it out here. Chapultepec (2018). Linen. 24 components, each component 800 cm. Sheila Hicks…
5 great children’s spaces in the Bay Area, California
I was fortunate enough to recently spend a month in California, mainly in and around San Francisco. During this time I visited a handful of children’s learning spaces and met with a bunch of lovely, passionate people working in both formal and informal learning contexts. The places listed below are places that I visited or that came highly recommended. I hope you find these equally as inspiring as I did! The Brightworks School Founded by Gever Tulley who also started The Tinkering School, Brightworks is a project-based learning heaven that ‘weaves learning and life experiences together.’ In the every day runnings of the school, children are put into mixed-aged group teams and encouraged to investigate real-world problems collectively. ‘The Arc’ (I interpret this term to mean the pedagogical principles that drive the learning processes at the school) consists of three phases: exploration, expression and exposition. Learners move through these cycles, allowing for…
Reggio Emilia Australia article on art, museums and creative learning
This post is an extract of a conversation between myself and Chris Celada published in the current edition of ‘The Challenge,’ Reggio Emilia Australia’s quarterly journal. Chris is a teacher and Reggio Australia editorial board member. The conversation offered the opportunity for both of us to dig deeper into our philosophies, strategies and practices of working at the intersection of art and pedagogy.
The Tinkering Studio at the Exploratorium in San Francisco, USA.
This post features a reflection on my visit to the Tinkering Studio at The Exploratorium in San Francisco, USA with a focus upon what art galleries can learn from the Studio’s approach to constructing immersive creative environments for children based on experiential learning and play. In August 2015 I participated in a ScratchJr/Light Play prototyping session between the MIT Media Lab’s Lifelong Kindergarten group and the Tinkering Studio team at The Exploratorium. The Tinkering Studio, which opened in 2008, is a research and design laboratory housed inside the Exploratorium, a museum devoted to the intersection of art, science and technology. The Studio is an “immersive, active, creative place” [2] for experimentation, investigation, making and hands-on play for all ages. Scientists, artists, programmers and academics frequently take up residence in the studio, working alongside the Tinkering Studio team to create new installations, run programmes and run public forums. I have closely followed the progression of the Tinkering Studio’s programme for…